Raisins Health Benefits | Raisins Nutrition Facts
- Introduction
- What Are Raisins?
- Varieties Of Raisins
- Raisin Nutrition Facts
- Raisins Health Benefits
- Are Raisins Good For Health?

Introduction
Every box of raisins is a tragic story of grapes that could have been wine.
~ Unknown
I can’t entirely agree with the quote above, and by the end of this article, everyone will agree that the best way to consume grapes is to eat them naturally or as raisins, full of fiber and nutrients. 1https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30106463/
What Are Raisins?
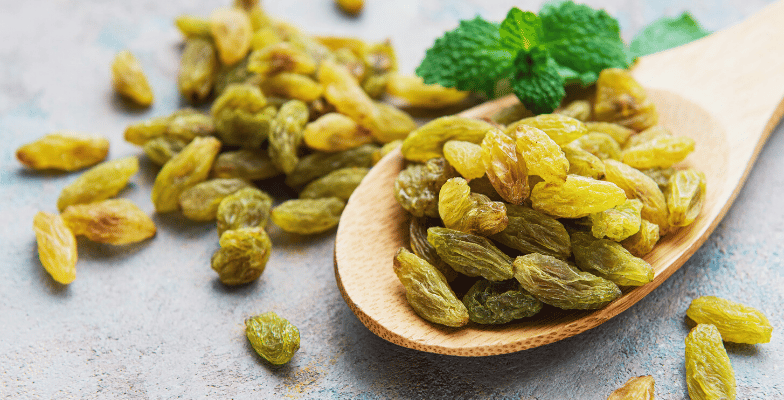
Raisins are dried grapes from the Vitis vinifera L variety. They are eaten as a snack in trail mix and granola, used as a topping for yogurt or cereals, and added extensively to cakes and bread.
Raisins are storehouses of nutrients like protein, carbohydrates, fats (lipids), fiber, sugar, calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, zinc, vitamin K, vitamin E, vitamin B6, niacin, and riboflavin.
The sweetness and stickiness of raisins make them a favorite snack among young and old and healthy alternatives to commonly consumed sugary snack foods. There are many different types of raisins with different shapes, colors, sizes, and flavors.
Varieties Of Raisins
Natural Seedless Raisins
These are from Thompson seedless grapes and account for almost all the raisins grown in California. They are green grapes that turn brown as they dry in the sun.
Sultanas
They are from seedless yellow-green grapes, soft and tart in taste.
Currants
These are from black Corinth grapes, smaller in size, seedless, dark in color, and tangy in taste.
Flame Seedless Raisins
They are large, dark red, extra sweet, and from the flame seedless variety of grapes.
Golden Seedless
They are also Thompson seedless grapes but are treated with sulfur dioxide to preserve their light color.
Muscat Raisins
They are from Muscat grapes. They are fruity in taste, have seeds, and are used in baking.
Monukka Raisins
These are from grapes with the same name, are large, dark, seedless, and mostly grown and available in Asia.
Once harvested, grapes are cleaned, washed, selected, and sorted out. They are pretreated physically or chemically to improve the grape skin, drying process, and raisin quality. Let’s look at the nutritional value of raisins.
Raisin Nutrition Facts
Since raisins are dried grapes, their nutritional content is similar to grapes. Raisins have a higher concentration of antioxidants than grapes and a lower vitamin C because of the drying process. According to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) 2https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/168165/nutrients, the nutritional facts for a serving of raisins (1.5 ounces, a small box or 40-50g)
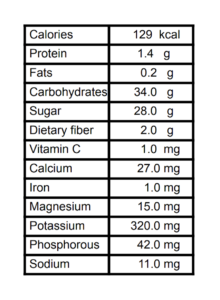
Raisins are sweet as they are about 60% sugar, mostly fructose and glucose. Their sugar content gives rise to the misconception that they are unhealthy. Studies do not agree, so let’s look at the health benefits of raisins.
Raisins Health Benefits
Oral Health
Dental decay depends on several factors, including our health, diet, and microbial infection. Besides dental caries, gingivitis and periodontal disease also affect the adult population, especially with increasing age.
Raisins contain oleanolic acid, which stops the growth of streptococcus mutans, bacteria found in the mouth responsible for tooth decay. Oleanolic acid also helps prevent plaque and periodontal disease. 3https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5642187/
Raisins are sweet and sticky and are not considered suitable for dental health. But studies show a weak correlation between stickiness and clearance of food particles from the tooth surface after chewing and swallowing. 4https://calraisins.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/45-Wu_2009-Grape-products-and-oral-health.pdf
Low Glycemic Index
A low glycemic diet can help control weight by minimizing spikes in blood sugar and insulin levels. Low glycemic foods reduce the risk of high blood pressure and heart disease and improve glycemic and cardiovascular markers, including HbA1c. 5https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30531821/
The fructose in raisins has a glycemic index (GI) of 15 ± 4, which is very low and healthy. Studies show raisins do not promote a significant insulin response in healthy individuals. 6https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4153099/
Blood Pressure And Heart Health
High blood pressure is a risk factor for hypertension, which affects our health in many ways. Raisins are high in dietary fiber, potassium, polyphenols, phenolic acid, tannins, and antioxidants, which help reduce blood pressure, total cholesterol, and LDL. 7https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22931531/ , 8https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24393750/ A study highlighted the benefits of red grapes and raisins in improving lipid profile and kidney functions. 9https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30106463/
Antioxidant
We know raisins are a source of polyphenols, phenolic acid, and glycosides, all of which act as antioxidants. Studies suggest that antioxidants in raisins from Vitis vinifera grapes may prevent cells from age-related physical destruction and degeneration, leading to memory impairment. 10https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20041785
The amount of antioxidants, including polyphenols, phenolic acids, and tannins, is higher in raisins than in juice alone due to the amount of sugar and beneficial minerals such as potassium, calcium, and iron in whole grapes. Hence eating grapes or raisins provides more antioxidants than drinking wine. 11https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6195892/
The levels of total phenolic compounds differ between varieties of raisins. White raisins have the lowest level, and red raisins have the highest. The distribution of polyphenolic compounds in raisins is about 5% in the juice, 1% in pulp, and the balance in the seeds. 12https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6356098/
Colon Health
Researcher Gene A. Spiller showed that 2 servings of raisins (84 g/day) could be beneficial to colon function and may decrease colon cancer risk. The study suggested that sun-dried raisins are a good source of dietary fiber, tartaric acid, good stool softeners, and shorten intestinal transit time.
They may increase fecal weight, the composition of fecal bile acids, and short-chain fatty acids (SCFA), all beneficial for gut health. 13https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/13129449/, 14https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12935318/
Are Raisins Good For Health?
Yes, overall, we can conclude that raisins, which are low to medium energy-dense and loaded with vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber, are an excellent option to eat daily in moderation. Also, added sugar intake is lower in those who eat raisins regularly as raisins replace other sugar sources.
The effects of raisin intake on blood pressure, lipid profile, glucose, oxidative damage, and satiety are well-established in various studies. Raisin juice concentrate is also a sweetener, binding agent, coloring, and flavor enhancer for cereal bars.
Nutritionally it is a better option than artificial sweeteners. Those who are watching their calories can keep an eye on the number of raisins they are eating. They are small but are calorie-dense.
What do you think about this article? Have any questions? Let me know in the comments below!

Skill-Based Education.
Global Recognition.
Powerful Community Building
Secure a certificate of completion in as little as a day by graduating from one of our free courses.
Get Access to Our Free Courses. No Credit Card Required.
Fabulous Body Membership
Your All-Access Pass to A Fabulous Body & A Rewarding Career
25+ Certificate Courses & Programs, All Included
15 Day Free Trial, 100% Money-Back Guarantee
About Kamini Thakar
Kamini is a very skilled writer/content creator. As a part of Fabulous Body for years, she has authored many articles really proving her prowess in acquiring and presenting knowledge about various health & nutrition topics.










