What Is Quinoa? | Quinoa Nutrition Facts And Health Benefits
- What Is Quinoa?
- Nutritional Properties Of Quinoa
- Quinoa Health Benefits
- Downsides Of Eating Quinoa
- Conclusion And My Suggestion
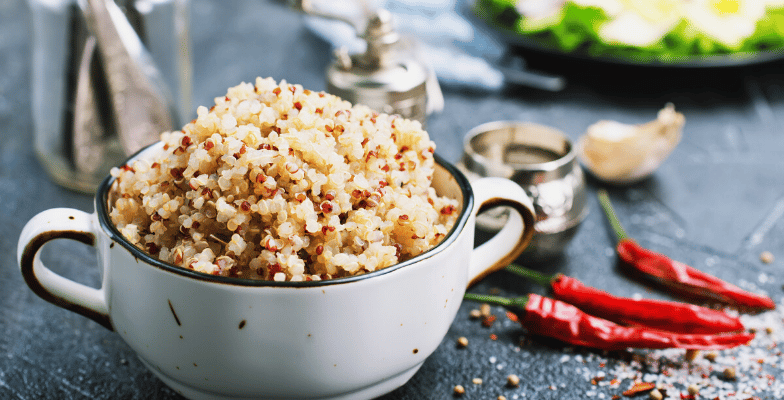

Two decades ago, I didn’t think many people could have identified, pronounced, or would have eaten the tiny round grain similar to sesame seeds called quinoa (pronounced KEEN-wah).
But by the early 2000s, quinoa had taken the natural food market by storm and created a niche for itself, claiming a space in the healthy grain aisles of grocery stores. It has gained attention globally due to its nutritional and functional values and its ability to be grown under diverse climate conditions.
In this article, we will learn why quinoa is replacing and becoming a healthier alternative to wheat and rice in the current diet scenario.
What Is Quinoa?
Quinoa, a herbaceous plant, is one of the oldest native crops of South America’s Andean region. It is known as ‘golden grain,’ though the word quinoa means ‘mother grain‘ in the Inca language.
Quinoa is a seed, not a grain. Still, it has been called a pseudocereal, not just for botanical reasons but also because of its grain-like characteristics and exceptional balance between oil, protein, and fat.
Quinoa comes in more than 100 varieties and various colors; however, the versions most commonly available in grocery stores are black, red, yellow, and white.
Quinoa can be consumed similarly to rice, prepared in soup, puffed to make breakfast cereal, and as an ingredient in energy bars. It is grounded in flour to produce toasted and baked goods like cookies, bread, biscuits, noodles, flakes, tortillas, pancakes, and pasta.
Quinoa seeds are fermented to make beer or a traditional ceremonial alcoholic beverage from South America called chicha. The United Nations (UN) and World Health Organization (WHO) declared 2013 ‘The International Year of Quinoa’ due to quinoa’s fantastic nutrient value and potential to contribute to food security worldwide for present and future generations.
According to Medical News Today, NASA scientists contemplated growing the protein plant in outer space since it is easy to plant and maintain and most nutritious. 1https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/274745
Nutritional Properties Of Quinoa
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) observed that quinoa seeds have high-quality proteins and provide more energy, calcium, phosphorus, iron, fiber, and B vitamins than barley, oats, rice, corn, or wheat.
Genetic variations and environmental conditions are two factors that may affect the crop and nutritional quality of quinoa.
Protein & Amino Acids
Quinoa’s protein content ranges from 11% to 19%, depending on the crop’s variety and the environment where it is grown. Most importantly, quinoa seeds contain all nine essential amino acids (EAA) for proper health.
Quinoa has acquired attention as a protein source due to the high quality and balanced composition of its protein—superior to wheat, barley, and soybeans.
Carbohydrates & Fiber
Quinoa’s main carbohydrate element is starch, which has maximum viscosity, a higher water absorption capacity, and a bigger swelling capacity than starches of wheat or barley. In addition, Quinoa is a complex carbohydrate, which means it is digested slowly, giving the body time to absorb nutrients and not quickly convert them into sugar and fat.
Quinoa has a high dietary fiber content compared with other grains, providing 5.18 g in a single 185 g cup, which is about 15.42% of a person’s daily requirement. Dietary fiber is essential for good digestion and to prevent constipation.
Related Article: What Is Fiber? Health Benefits, Food Sources And Daily Requirements
Fats
Fats are an essential source of calories and aid in absorbing fat-soluble vitamins. Quinoa contains 2-10% fat and essential fatty acids such as linoleic acid (52.3 %), linolenic (3.9%), and oleic acid (24.8%). Quinoa is a healthy oily seed due to its quality and quantity of lipid fractions. 2https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/0308814694902550#:~:text=Total%20lipids%20composition&text=Neutral%20lipids%20accounted%20for%2040.2,9%25%20in%20whole%20quinoa%20seed
Minerals
Quinoa’s ash or mineral content (2.7g/100gm) is higher than rice’s (1.7g/100gm), wheat’s (1.8g/100gm), and most other grains. 3https://nutraceuticals.imedpub.com/quinoa-nutritional-aspects.pdf
Vitamins
Quinoa is a good source of vitamin B1 (0.4 mg/100 g), vitamin B9 (78.1 mg/100 g), vitamin C (16.4 mg/100 g), and vitamin E in the forms of γ-tocopherol (5.3 mg/100 g) and α-tocopherol (2.6 mg/100 g). Quinoa contains more vitamin B2 and α-tocopherol than rice, barley, or wheat. 4https://www.agriculturejournals.cz/publicFiles/06732.pdf
Quinoa Health Benefits
Studies suggest quinoa may benefit high-risk groups, such as children, the elderly, high-performance sportspeople, individuals with lactose intolerance, and celiac disease due to its properties, including its high nutritional value and gluten-free content.
Improves Gut Health
Quinoa is rich in high-quality protein, vitamins, minerals, and especially various polysaccharides. It has a prebiotic effect, which means it aids the growth of useful bacteria and short-chain fatty acids.
Studies suggest quinoa may have beneficial effects on intestinal health. Polysaccharides from quinoa have demonstrated immune-regulating activity in animal studies. 5https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6175902/
Diabetes
Quinoa contains 10% of the Required Daily Intake (RDI) of fiber and 80-90% of its insoluble fiber. Fiber helps with appetite control and satiety. Quinoa has a low glycemic index of 53, which may help prevent obesity and type 2 diabetes. Research also shows quinoa may be useful in managing blood sugar in people with diabetes.
Gluten-Free
As a gluten-free pseudocereal, quinoa is suitable for people who cannot tolerate or are allergic to gluten. 6https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15309439/ A recent laboratory test suggested quinoa contains proteins similar to gluten to activate patients’ immune systems with celiac disease. Celiac patients often have an iron deficiency due to a gluten-free diet, but quinoa is rich in iron, making it an up-and-coming alternative to wheat. 7https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4957693
Strengthens Bones
A sufficient intake of magnesium, copper, phosphorus, potassium, zinc and calcium is required to build bones and prevent osteoporosis. 8https://americanbonehealth.org/nutrition/minerals-for-bone-health/ One cup of quinoa contains 20 – 30% of the RDI of most of these minerals.
Good For Skin
A study reported in The International Journal of Dermatology found that in addition to vitamins C and E, zinc plays a vital role as an antioxidant that protects against skin cancer and keeps the skin in good health. 9https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1046/j.1365-4362.2002.01567.x One cup of quinoa has 13% of the RDI of zinc, which protects the skin against ultraviolet rays and helps heal faster. 10https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4120804/
Antioxidants
Quinoa is one of the best gluten-free vitamin E sources, an antioxidant component that may reduce coronary heart disease and certain cancers. 11<https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6024323/
Quinoa contains the plant compounds quercetin and kaempferol, which act as antioxidants. Kaempferol may help protect the body against infection, heart disease, diabetes, and several cancers, including those of the skin and liver.
Quercetin has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antidepressant properties. 12https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6631472/ Quinoa polysaccharides are excellent dietary sources of natural antioxidants that promote health. 13https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4227275/
Downsides Of Eating Quinoa
Eating quinoa may have a few downsides. However, a few precautions can take care of these.
Upset Stomach
Quinoa seeds have a protective layer of bitter, unpalatable saponins, quinoa’s natural defense against pests, bacteria, and fungi. If not removed, says the horticulture department at Purdue University, saponins can lead to an upset stomach and interfere with the small intestine function. It is essential to wash quinoa a few times before consuming it.
Prohibits Mineral Absorption
Quinoa contains minerals like magnesium, phosphorus, copper, zinc, and folate. Unfortunately, it is also high in phytic acid, which blocks the entry of minerals into the bloodstream. This issue can be remedied either by fermentation or soaking quinoa seeds before consuming them.
Oxalates
Quinoa belongs to the same plant family as beetroot and spinach and has a high oxalate content, a common cause of kidney stones. Most kidney stones consist of calcium oxalates.
Conclusion And My Suggestion
From a nutritional perspective, quinoa is a highly nutritious grain loaded with minerals, fiber, amino acids, carbohydrates, and protein, including all nine essential amino acids. Not only is quinoa gluten-free, but it’s also easy to digest, and for vegetarians and vegans, it is the perfect alternative to animal protein.
I strongly advise including quinoa in a balanced diet with rice, wheat, grains, and other pseudocereals like amaranth, chia, and buckwheat for good overall nutrition.
What do you think about Quinoa? Do you have any questions? Let me know in the comment below!

Skill-Based Education.
Global Recognition.
Powerful Community Building
Secure a certificate of completion in as little as a day by graduating from one of our free courses.
Get Access to Our Free Courses. No Credit Card Required.
Fabulous Body Membership
Your All-Access Pass to A Fabulous Body & A Rewarding Career
25+ Certificate Courses & Programs, All Included
15 Day Free Trial, 100% Money-Back Guarantee
About Kamini Thakar
Kamini is a very skilled writer/content creator. As a part of Fabulous Body for years, she has authored many articles really proving her prowess in acquiring and presenting knowledge about various health & nutrition topics.











This article describes the useful information about Quinoa in a very simple and easy to read manner. I enjoyed reading it and I intend to look into adding Quinoa to my food.
ma’am awesome article…after reading it i have no further questions about the pseudo cereal…
I am just curious were u on the documentary HEAL by any chance?
Hello Sir
Sir i have a question.
When someone has a thyroid problem, what should be taken in the diet to gain weight?
What should be the diet plan?
Thanks
Thanks, Bhanupriya.
No, I was not in the documentary.