Pear Nutrition | Health Benefits Of Pear
- Introduction
- Health Benefits Of Pear
- Pear Glycemic Index
- Pear Vs. Apple
- Varieties Of Pear
- Conclusion And My Recommendation
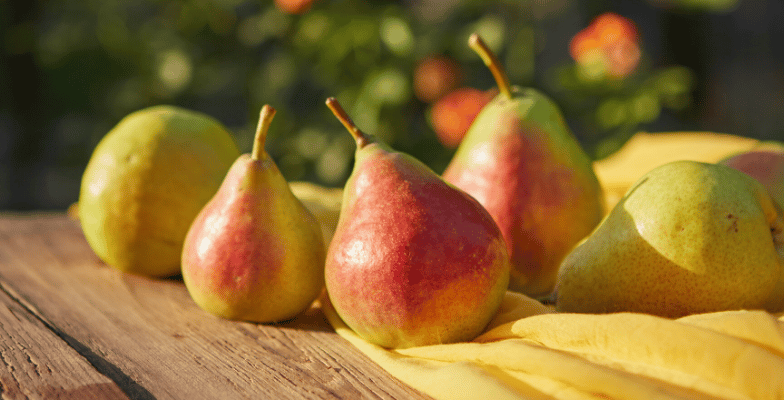

Introduction
A pear is a failed apple.
~George Carlin
When it comes to taste, one might prefer apples, but pears are as good as apples if nutrition is the deciding factor. So no! Pear is not a failed apple.
The pear tree and shrub are a variety of the genus Pyrusin the Rosaceae (rose) family. Pears are often called pome fruits, which means they have a core of several small seeds surrounded by a tough membrane.
Pears are known for their bell shape, wide on the bottom and tapered up top with a thin exterior skin and soft, juicy flesh. One of the essential fruit trees grown globally, many pear trees are cultivated for their fruit and juice, while others are conserved trees.
Pears are natives of Europe and West Asia and were introduced to North America in the 17th century. They have been used as a traditional folk remedy in China for over 2,000 years because of their reported anti-inflammatory, antihyperglycemic, and diuretic qualities.
Health Benefits Of Pear
May Promote Gut Health
Pear is an excellent source of soluble and insoluble fiber, which is good for digestive health. Consuming fiber-rich foods is essential as it helps maintain bowel regularity by bulking up and softening the stool.
Pear skin contains a great deal of fiber and flavonoids, and it may be best to eat this fruit unpeeled. 1https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18778075/ A single medium-sized pear (178 g) contains about 6 g of fiber, 22% of daily fiber needs. 2https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169118/nutrients Pears comprise a soluble fiber called pectin, which nurtures gut bacteria and improves gut health. 3https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3705355/
The latest research by Dr. Shetty of North Dakota State University suggests that pear has potential probiotic benefits that may help delay diseases like type 2 diabetes and its associated cardiovascular complications. 4https://www.outlookindia.com/newsscroll/new-research-investigates-potential-probiotic-benefits-of-pearenriched-diet/1227149
Related Article: What Is Fiber? Health Benefits, Food Sources And Daily Requirements
May Have Anticancer Effects
Flavonoids are a varied group of phytonutrients (plant chemicals) found in almost all fruits and vegetables, responsible for their remarkable variety of colors. 5https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5465813/, 6https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12936950/
Various studies suggest that flavonoids in pears, like quercetin and hydroxycinnamic acid, may significantly prevent gastric, esophageal, colorectal, prostate, lung, and breast cancers. 7https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/79/5/727/4690182, 8https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11078758/https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18491402/
May Reduce The Risk Of Cardiovascular Disease
Pears offer many beneficial compounds that may improve heart health and strengthen blood vessels. 9https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23522824/ While eating more fruit and vegetables may reduce cancer and CVD risk, it is not a replacement for medical treatment.
A 2019 study on pears noted that people with insulin resistance syndrome who consumed two pears a day for 12 weeks saw a modest decrease in systolic blood pressure and pulse pressure. We know high blood pressure is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. 10https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30720034/
A 10-year comparative study of over 20,000 people ages 20-65 with no heart health issues suggested that every 25g of white-fleshed fruits like apples and pears eaten daily decreased stroke risk by 9%. 11https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21921279/
May Reduce The Risk Of Diabetes
A doctor may refer a person with diabetes or prediabetes to a nutritionist who can help the person lead an active, balanced lifestyle and manage the condition. A study of half a million people in China suggested that those who ate fruit, including pears, were 12% less likely to get type 2 diabetes than those who rarely ate the fruit. 12https://www.nhs.uk/news/food-and-diet/daily-diet-of-fresh-fruit-linked-to-lower-diabetes-risk/
The research also found that fruit eaters who already had diabetes at the start of the study were slightly less likely to die or to get complications like eye problems (diabetic retinopathy) than those who ate fruit rarely or never. 13https://www.nhs.uk/news/food-and-diet/daily-diet-of-fresh-fruit-linked-to-lower-diabetes-risk/
One animal study model for type 2 diabetes found that anthocyanins present in pears were significantly linked to decrease blood glucose concentrations and improve insulin sensitivity. A follow-up study by the NHS found that fruits with higher bulk of anthocyanin were associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes. 14https://depts.washington.edu/nutr/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Pears-2013.pdf
Pear Glycemic Index
The glycemic index (GI) can help assess how food with carbohydrates raises blood glucose levels. It is crucial to consume foods on the low or medium end of the GI spectrum as much as possible.
The GI measurement for specific foods depends on many factors, including how much fat and fiber they contain and the cooking method, ripeness, and how they are processed.
Related Article: What Is Glycemic Index | Food List With Glycemic Index
According to Diabetes Care and the organization USA Pears, a medium-sized pear has a glycemic index of 38 and a glycemic load of 4. That makes it a low-GI and GL food, mostly because of its high fiber content. 15https://usapears.org/pears-and-diabetes-2
Pear Vs. Apple
While pears and apples have almost the same nutrients and minerals, the pear is not as beautiful as its sibling and does not deserve respect. Both apples and pears are from the same Rosaceae family, and both were first cultivated in Asia.
And while their outward appearances are different, they have similar skin coverings and sweet, white insides. Though pears’ and apples’ carbohydrate and sugar count seems high, they are excellent foods to snack on while on a diet.
Most fruits have high levels of sugar but are generally low on the glycemic index. That means they help steady blood sugar levels throughout the day and prevent feelings of hunger.
With high fiber content, pears, like apples, help promote feelings of fullness and regulate digestion. Since pears have less sugar and more fiber than apples, they will do a better job of moderating hunger.
Both fruits are full of fiber and rich in antioxidants, the right things to keep the body running at its best. When it comes down to which fruit to eat, a preference in taste is sure to be the deciding factor.
Varieties Of Pear
There are over 3,000 cultivars of pears around the world. They vary in size, shape, sweetness, and crispness. Some common types of pear are.
Asian
Asian pears have a crisp texture, light brown skin, and a mild sweet taste. There are many Asian pear varieties, though Hosui and Nijisseki tend to be the most popular.
Bosc
Bosc pears have a matte look to their skin, with light brown patches overlaying the green skin beneath. They’re highly aromatic and hold their shape well when sliced into dishes (for example, when baked into a pear tart).
Comice
These are a combination of Asian and Bosc pears in tartness, fruitiness, and softness. They don’t have a grainy texture and are wide and round at the bottom.
Bartlett
Also known as Williams Pears, these are super soft and one of the juiciest varieties of pear. They are available in red and green colors and are the classic lunch box variety of pear.
Anjou
They are the mild, common variety and are available as red Anjou or green Anjou though there’s no marked difference in taste between them. Red Anjou pears have a burnished rusty color and are slightly more elongated than the green variety.
Forelle
One of the smaller, more snackable varieties of pear, Forelle pears display an example of pear freckles, which occur in bright red stripes over light green flesh.
Concorde
These pears are bright green with a long, tapered shape and a hint of blush color around the bottom section. They’re delightful and sweet throughout the ripening stage with a faint vanilla flavor.
French Butter
A delicate European variety that’s perfect for making pear butter. French Butter pears turn pale gold when ripe and have a creamy, juicy texture.
Seckel
Seckel pears are a two-to-three-bite kind of pear that fits in the palm. Thanks to their size and firm flesh, they are used for baking and canning.
Conclusion And My Recommendation
Pears are as good as a fruit can be, nutritional powerhouses, and a source of natural prebiotic fiber, delicious and inexpensive. Due to their health benefits, including pears in our daily diet is a no-brainer.
What do you think about the article? Have any questions? Let me know in the comments below!

Skill-Based Education.
Global Recognition.
Powerful Community Building
Secure a certificate of completion in as little as a day by graduating from one of our free courses.
Get Access to Our Free Courses. No Credit Card Required.
Fabulous Body Membership
Your All-Access Pass to A Fabulous Body & A Rewarding Career
25+ Certificate Courses & Programs, All Included
15 Day Free Trial, 100% Money-Back Guarantee
About Kamini Thakar
Kamini is a very skilled writer/content creator. As a part of Fabulous Body for years, she has authored many articles really proving her prowess in acquiring and presenting knowledge about various health & nutrition topics.










