Good Carbs Vs. Bad Carbs | Complete List
- Introduction
- List Of Good Carbohydrate Sources
- List Of Bad Carbohydrate Sources
- Conclusion & Final Thoughts
Whether you are intensely focusing on finishing your elusive last piece of Rubik’s cube or pulling an all-nighter to finish off your pending assignment, your brain demands carbohydrates to fuel this activity.
More so, this demand increases, not necessarily in a linear fashion, with the intensity of the activity in question. It can be grooving to your favorite music or playing a tennis game with your friends. Your body needs carbohydrates, either in glucose or its stored form, glycogen.
Introduction
As clichéd as it may sound, the statement ‘all carbohydrates are not equal’ certainly has merit. The above statement has been the basis for the perennial battle between the supposedly ‘good’ carbohydrates and the ‘bad’ carbohydrates.
For the uninitiated, carbohydrates are organic compounds comprising carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The carbohydrate family consists of not only starches and sugar but also fiber.
Related Article: Side Effects Of Sugar: How Much Can You Eat In A Day?
This macronutrient group is so pervasive in our diets and so hard to resist that hardly a meal goes by which is devoid of any carbs; maybe that’s why it has been a scapegoat to cover all the other wrong food choices we make daily.
As you start discerning the differences among the various forms of carbohydrates on the menu, you will surely be in a better position to make healthier food choices, boost your mental and physical performances, or lose weight. To evaluate carbs objectively, we can use multiple metrics to identify specific characteristics that can help us classify them in either category.
One key metric is whether it is a simple carbohydrate (containing a single or double molecule of sugar) or a complex carbohydrate (containing multiple sugar molecules).
Generally speaking, simple carbs are mostly empty calories (except fruits). Most of the food we label junk falls in this simple carb category- calorie-rich and nutritionally deficient.
Complex carbs are full of antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, or naturally acting antioxidants like phytochemicals, which simple carbs usually lack.
The second metric can be using the Glycemic Index. Simply speaking, it is the rate at which food gets converted to glucose post-consumption. A number is assigned, on a scale of 1-100, to each carbohydrate source, with a higher number indicating a faster conversion and a rapid rise of blood glucose levels in the blood.
Glucose serves as a reference point at a Glycemic Index of 100. The Glycemic Index (GI) used in conjunction with the glycemic load, which takes into account the amount of carbohydrate consumed, lends better results to estimate the actual rise in blood glucose levels.
Foods with a high GI raise blood glucose faster than low GI Foods and can cause insulin to surge rapidly. Wild insulin swings for a prolonged period can have severe cardiovascular repercussions and even obesity.
This metric does have its shortcomings, though, and provides a general rule of thumb, and the complete nutritional profile of the food/cooking method/ mixed foods in the dish, in reality, affects the overall GI. Be mindful of this caveat when designing diet programs.
Related Article: What Is Glycemic Index | Food List With Glycemic Index
Third, the amount of fiber in carbohydrates is another robust metric, with high-fiber-content foods qualifying in the good carbohydrate category. Fiber is essential for overall better health aids in better digestion, and prevents constipation, alongside being a top contender for promoting weight loss through indirectly suppressing appetite.
Related Article: What Is Fiber? Health Benefits, Food Sources And Daily Requirements
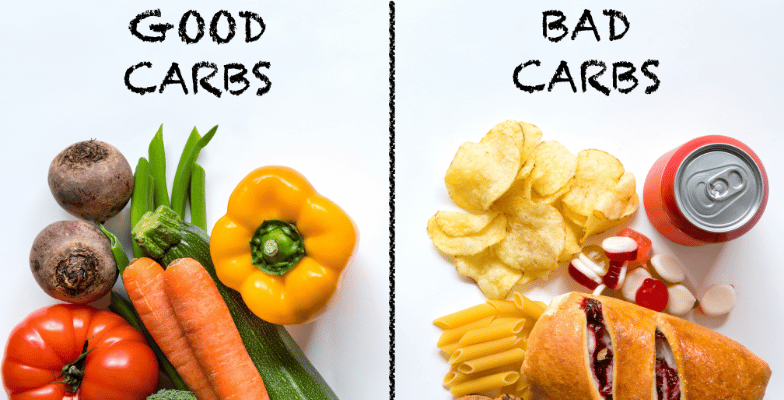
So keeping these characteristics in mind, let’s discuss the list of good carbohydrates and bad carbohydrates.
List Of Good Carbohydrate Sources
Oatmeal
No Healthy Food list can be complete without such a staple breakfast item. Though many are not particularly fond of the bland natural flavor it offers, there are many other benefits it has to offer.
This study has found significant evidence strengthening the associated relationship between the consumption of oat beta-glucan ( a soluble fiber occurring in oats) and the corresponding decrease in blood cholesterol. 1https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21631511/ Additionally, it is highly satiating, which aids in weight loss and helps control Type 2 diabetes. 2https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4690088/#:~:text=Oatmeal%20significantly%20reduced%20the%20acute,in%20type%202%20diabetic%20patients, 3 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4757923/
Sweet Potato
Sweet Potato is undoubtedly one of the most nutritious vegetables you can lay your hands on. The bright orange color is a consequence of the high beta-carotene content, an antioxidant that gets converted to Vitamin A post-consumption.
Vitamin A, in addition to supporting a healthy immune system, also helps maintain good vision. 4https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1039942/ Although it tastes sweet, it has a moderate ~86 calories per 100g of serving with almost no fat.
Legumes
Legumes are one of the most nutritious options for vegetarians, with an impressive food profile. Legume refers to the seeds of the plants which produces pod, such as chickpeas, beans, peanuts, and soybeans. They are packed with ample complex carbohydrates and protein and help reduce cholesterol levels. 5https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2888631/
The complex carbohydrates allow slow down gastric emptying allowing the steady release of insulin, which stabilizes blood sugar levels. When you have steady blood sugar levels, there are no cravings, which ultimately leads to weight loss!
Berries
Besides tasting heavenly, raspberries, strawberries, and blueberries, blackberries are also one of the healthiest fruit carbs loaded with antioxidants that help fight heart diseases. 6https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3068482/#:~:text=Berries%20are%20a%20good%20source,with%20improved%20cardiovascular%20risk%20profiles In addition, they also contain a phytochemical called ellagic acid, which can help to prevent cancer, as per this research.
Blueberry supplementation has also been shown evidence to improve memory and avoid dementia in adults, as per this research published in 2010. 7https://www.researchgate.net/publication/40846333_Blueberry_Supplementation_Improves_Memory_in_Older_Adults Berries can be added to other dishes for a quick, delectable snack and also turn up the aesthetic appeal of the meal.
Brown Rice
Unlike stripped white rice, brown rice is a whole grain that is not stripped of its nutritional value in the process of preparation. It is essentially made whole by the presence of the outer bran layer, the germ- which is the core of nutrients, and the endosperm refers to the middle layer.
In addition to lower calorie contribution, it has good fiber content and is also low on the Glycemic Index, ticking all our carbohydrate metrics.
Wheat Bran
Wheat bran refers to the part of the wheat kernel which gets removed during the milling process and is usually considered a byproduct but has a lot to offer to owe to its nutritionally dense profile.
It is low in calories at ~60 calories for 30g servings and meets the daily recommended fiber requirement in just about 30g. The digestive system also gets a boost owing to the insoluble fiber, which can aid in normal bowel movement and prevent constipation.
Greens
They feature in the superstar list of the nutritional heroes of all time. Kale, spinach, cabbage, and beet greens are some of the most popular ingredients for a healthy meal. They are super rich in Folate & beta-carotene, especially spinach.
Consumption of dark green leafy vegetables has been shown to lower the risk of cancer and even help delay cognitive decline. 8https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8988807/, 9https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0197458004801829?via%3Dihub They also have an abundance of vitamins Like Vitamin E & Vitamin C, which keeps the skin tissue healthy and regular consumption also reduces the risk of cataract. 10https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25591715/
Bananas
Hypothetically speaking, If there were an award for the tastiest, healthiest and cheapest fruit option, bananas would come second to none. They are considered mood booster carbohydrates for a reason.
They are endowed with magnesium, which tends to get depleted after bouts of severe stress periods. Bananas help replenish these magnesium reserves and also help make the mood better. The amino acid tryptophan is also present, which helps improve serotonin metabolism, which regulates mood and social behavior.
List Of Bad Carbohydrate Sources
There are certain sources of carbohydrates that one should avoid or consume in moderation.
White Rice
Unlike brown rice, white rice is a refined or nutrient-stripped version of brown rice. The stripping removes the germ (nutrient core) and the bran leaving just the endosperm. The process also removes other nutrients like Iron, B vitamins, and iron, according to the American Heart Association. 11https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/nutrition-basics/whole-grains-refined-grains-and-dietary-fiber#.W7OWcJNKjBI
The relatively higher GI also makes it a less preferred choice and may increase the case of type 2 diabetes. 12https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4144100/ It is not bad when mixed with other low GI foods, but it is better to switch to healthier brown rice for an overall better nutritional profile.
Refined Pasta
As opposed to whole grain pasta, refined pasta is often consumed, which is high in calories and highly deficient in fiber and, again, does not lend satiety to the food. It is also a form of simple carbohydrate that rapidly raises blood glucose levels and can trigger overeating and even weight gain.
Sugar-Sweetened Beverages (SSBs)
SSBs are probably the number one candidate who is wreaking havoc in your diet plans. Drinks like artificial fruit juices, and carbonated beverages are incredibly high in added sugar. Some of them also provide fructose in ample amounts.
Since fructose does not lower the hormone ghrelin (ghrelin hormone primarily regulates hunger and sends signals to the brain to act hungry), it does not lend a fullness post-consumption, unlike foods high in fiber.
This may lead to surplus calorie intake, and also possibly overeating and regular excess consumption of such foods can be a cause of serious concern.
Related Article: Side Effects of Sugar: How Much Can You Eat In A Day?
Breakfast Cereals
By touting cereals as a healthy option, it is easily one of the most misleading claims made by breakfast cereal companies trying to offload sugar-laden foods to the unsuspecting and naïve consumer. Most ready-to-eat breakfast cereals are packed with large refined grains and sugars, which are precisely the opposite of what healthy foods are supposed to be, and that is devoid of sugars.
They are not the best option out there by any yardstick. A simple fruit like an apple or a banana with steel-cut oats will prove to be a tastier and healthier snack.
Ice Creams
This sugary and calorie-dense delectable sweet surely tops the list of all comfort foods. Despite how tempting and irresistible a tub of ice cream feels, you should also be concerned about how the sugars and extra additives wreak havoc in your body.
As per USDA, a 100g serving of ice cream has around ~22 grams of sugar with about ~215 Kcal. This study links excess sugar consumption and health conditions such as fatty liver disease and obesity. 13https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5133084/
Besides being calorie-dense and nutrient-deficient, ice creams are laden with several artificial flavors and additives. FDA has banned one such synthetic flavoring agent called Benzophenone. 14https://www.fda.gov/food/cfsan-constituent-updates/fda-removes-7-synthetic-flavoring-substances-food-additives-list
Conclusion & Final Thoughts
To summarize, in a nutshell, emphasize complex carbohydrates over simple carbohydrates and opt for fiber-rich fruits and vegetables over refined grains and processed foods.
You can always use the above-described metrics of simple vs. complex carbohydrate, Glycemic Index, and fiber content of the food item when in a quandary. There is a more straightforward test to determine if your food is possibly healthy or not.
Just ask yourselves, can you source this item from a farmer directly? If your answer is yes, your food choice is most likely healthy and nutritious. With this basic nutritional knowledge, you are more than equipped to make better food choices for yourself and your loved ones and lead a happy and healthy life.
What do you think about this article? Have any questions? Let me know in the comments below!

Skill-Based Education.
Global Recognition.
Powerful Community Building
Secure a certificate of completion in as little as a day by graduating from one of our free courses.
Get Access to Our Free Courses. No Credit Card Required.
Fabulous Body Membership
Your All-Access Pass to A Fabulous Body & A Rewarding Career
25+ Certificate Courses & Programs, All Included
15 Day Free Trial, 100% Money-Back Guarantee










